The Role of Baseline Glucocorticosteroid Therapy in Forming Metabolic Disorders in Patients with Bronchial Asthma
The aim of the investigation is to study the incidence and clinical features of metabolic syndrome in patients with bronchial asthma (BA) in various ways of performing baseline therapy of glucocorticosteroids (GCS).
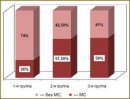
Materials and Methods. There have been examined 116 patients with medium and severe BA. The patients have been divided into three groups: the 1st group — 39 patients, who have not received baseline therapy; the 2nd group — 51 patients, who have taken medium and high doses of inhalation GCS for 2 years; the 3rd group — 26 patients, who have taken systemic GCS for 2 years.
Conclusion. BA is frequently associated with metabolic disorders. The rate and degree of manifestation of these disorders increase significantly against the background of GCS therapy. Visceral obesity, arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia and abnormalities of carbohydrate metabolism are the most common among other manifestations of metabolic syndrome in BA patients. Baseline therapy of inhalation GCS has its metabolic consequences including obesity, hyperinsulinemia, as well as insulin resistance development.
- Balabolkin M.I. Diabetologiya [Diabetology]. Moscow: Meditsina; 2000; 672 p.
- Butrova S.A. Ross Med Z 2001; 2(9): 56–60.
- Diagnostika i lechenie metabolicheskogo sindroma. Rossiyskie rekomendatsii VNOK [Diagnosis and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Russian recommendations SCRF]. Moscow; 2010; 28 p.
- Mitchenko E.I., Korpachev V.V. et al. Diagnostika i lechenie metabolicheskogo sindroma, sakharnogo diabeta, prediabeta i serdechno-sosudistykh zabolevaniy. Metodicheskie rekomendatsii [Diagnosis and treatment of metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, potential diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Methodological recommendations]. Kirov; 2009.
- Roytberg G.E., Ushakova T.I., Dorosh Zh.V. Kardiologiya 2004; 3: 94–101.
- Reaven G.M. The metabolic syndrome: requiescat in pace [Review]. Clin Chem 2005; 51: 931–938.
- Grundy S.M. et al. Definition of metabolic syndrome: report of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 2004; 109: 433–438.
- Eckel R.H., Grundy S.M. & Zimmet P.Z. The metabolic syndrome: epidemiology, mechanisms and therapy. Reviews the worldwide epidemiology, pathophysiology and management of the metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005; 365: 1415–1428.
- Yakovleva O.Ya., Zhamba A.O., Mazur Yu.V. Ratsional’naya farmakoterapiya 2008; 1(6): 64–67.
- Uryas’ev O.M., Panfilov Yu.A. Mezhdunarodnyy endokrinologicheskiy zhurnal 2008; 3(15): 15–25.
- Global’naya strategiya lecheniya i profilaktiki bronkhial’noy astmy [Global treatment approach and prevention of bronchial asthma]. Pod red. A.G. Chuchalina [A.G. Chuchalin (editor)]. Moscow : Atmosfera; 2007; 104 р7
- Voznesenskiy N.A. Ross Med Z 2008; 2(16): 65–68.
- Blokhin B.M. Farmateka 2006; 11(126): 60–66.
- Smolenov I.V. Pul’monologia 2002; 3(6): 10–15.










