Modern Technologies of Bacterial Biofilm Study
The aim of the investigation was to estimate the availability of new biomedical technologies to identify bacterial biofilms and evaluate them on a staphylococcal biofilm model.
Materials and Methods. We studied staphylococcal biofilms by mass spectrometry, laser scanning (confocal) microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, enzymatic and oxidative destruction of extracellular biofilm matrix.
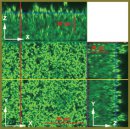
Results. We demonstrated the capabilities of new biomedical technologies in identification of generic specificity of biofilm-forming staphylococcus, and in detection of the necessary characteristics of staphylococcal biofilm. Mass spectrometry enabled to identify the type of biofilm-forming staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus). Microscopic study using laser scanning confocal microscopic technique revealed 3-demensional organization typical of S. aureus biofilms. Scanning electron microscopy enabled to visualize the structures of extracellular S. aureus biofilm matrix. The extracellular matrix of the test biofilm was found to be formed of DNA-protein complexes.
- Romanova Yu.M., Gintsburg A.L. Bakterial’naya bioplenka kak estestvennaya forma sushchestvovaniya bakteriy v okruzhayushchey srede i organizme khozyaina [Bacterial biofilms as a natural form of existence of bacteria in the environment and host organism]. Zhurnal mikrobiologii, epidemiologii i immunologii — Journal of Microbiology, Epidemiology and Immunobiology 2011; 3: 99–109.
- Mayanskiy A.N., Chebotar I.V. Stafilokokkovye bioplenki: struktura, regulyatsiya, ottorzhenie [Staphylococcal biofilms: structure, regulation, rejection]. Zhurnal mikrobiologii, epidemiologii i immunologii — Journal of Microbiology, Epidemiology and Immunobiology 2011; 1: 101–108.
- Gotz F. Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 2002; 43: 1467–1378.
- Vuong C., Otto M. Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Microbes Infect 2002; 4: 481–489.
- Frank K.L., del Pozo J.L., Patel R. From clinical microbiology to infection pathogenesis: how daring to be different works for Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2008; 1: 111–133.
- Fredheim E.G., Klingenberg C., Rohde H., Frankenberger S., Gaustad P., Flaegstad T., Sollid J.E. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus haemoliticus. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(4): 1172–1180.
- Bekhalo V.A., Bondarenko V.M., Sysolyatina E.V., Nagurskaya E.V. Immunobiologicheskie osobennosti bakterial'nykh kletok meditsinskikh bioplenok [Immunobiological features of bacterial cells of medical biofilms]. Zhurnal mikrobiologii, epidemiologii i immunologii — Journal of Microbiology, Epidemiology and Immunobiology 2010; 4: 97–105.
- Chebotar I.V., Mayanskiy A.N., Konchakova E.D., Lazareva A.V., Chistyakova V.P. Antibiotikorezistentnost’ bioplenochnykh bakteriy [Antibiotic resistance of biofilm bacteria]. Klinicheskaya mikrobiologiya i antimikrobnaya khimioterapiya — Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2012; 14(1): 51–58.
- Archer N.K., Mazaitis M.J., Costerton J.W., Leid J.G., Powers M.E., Shirtliff M.E. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2011; 2(5): 445–459.
- Jain A., Agarwal A. Biofilm production, a marker of pathogenic potential of colonizing and commensal staphylococci. J Microbiol Methods 2009; 76(1): 88–92.
- Taj Y., Essa F., Aziz F., Kazmi S.U. Study on biofilm-forming properties of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dev Ctries 2012; 6(5): 403–409.
- Chebotar I.V., Gurev E.L. Laboratornaya diagnostika klinicheski znachimykh bioplenochnykh protsessov [Laboratory diagnostics of clinically significant biofilm processes]. Voprosy diagnostiki v pediatrii — Diagnostic Issues in Pediatrics 2012; 4: 15–20.
- Mayanskiy N.A., Kalakutskaya A.N., Motuzova O.V., Lominadze G.G., Kryzhanovskaya O.A., Katosova L.K. MALDI-TOF mass-spektrometriya v rutinnoy rabote mikrobiologicheskoy laboratorii [MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in microbiological laboratory routine]. Voprosy diagnostiki v pediatrii — Diagnostic Issues in Pediatrics 2011; 3 (5): 20–25.
- Frank K.L., Patel R. Poly-N-acetylglucosamine is not a major component of the extracellular matrix in biofilms formed by icaADBC-positive Staphylococcus lugdunensis isolates. Infect Immun 2007; 75(10): 4728–4742.
- Izano E.A., Amarante M.A., Kher W.B., Kaplan J.B. Differential roles of poly-N-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Appl Environ Microdiol Biofilms 2008; 74(2): 470–476.
- Wang X., Preston J.F. III, Romeo T. The pgaABCD locus of Escherichia coli promotes the synthesis of a polysaccharide adhesin required for biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 2004; 186(9): 2724–2734.
- Flemming H.C., Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 2010; 8(9): 623–633.
- Jain A., Agarwal A. Biofilm production, a marker of pathogenic potential of colonizing and commensal staphylococci. J Microbiol Methods 2009; 76(1): 88–92.
- Chaignon P., Sadovskaya I., Ragunah Ch., Ramasubbu N., Kaplan J.B., Jabbouri S. Susceptibility of staphylococcal biofilms to enzymatic treatments depends on their chemical composition. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2007; 75(1): 125–132.
- Mack D., Fischer W., Krokotsch A., Leopold K., Hartmann R., Egge H., Laufs R. The intercellular adhesin involved in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis is a linear beta-1,6-linked glucosaminoglycan: purification and structural analysis. J Bacteriol 1996; 178(1): 175–183.
- Hansen U., Hussain M., Villone D., Herrmann M., Robenek H., Peters G., Sinha B., Bruckner P. The anchorless adhesin Eap (extracellular adherence protein) from Staphylococcus aureus selectively recognizes extracellular matrix aggregates but binds promiscuously to monomeric matrix macromolecules. Matrix Biol 2006; 25: 252–260.
- Montanaro L., Poggi A., Visai L., Ravaioli S., Campoccia D., Speziale P., Arciola C.R. Extracellular DNA in biofilms. Int J Artif Organs 2011; 34(9): 824–831.










