Morphofunctional Status of Erythrocytes in Cervical Cancer Patients after Femtosecond Laser Radiation Exposure
The aim of investigation was morphofunctional assessment of peripheral erythrocytes in cervical cancer patients (Ib–IIa stage) after femtosecond laser radiation exposure with different energy density.
Materials and Methods. We assessed membrane cytoarchitectonics, rigidity and the parameters of “lipid peroxidation–antioxidants” system using scanning probe microscopy and biochemistry. Femtosecond laser radiation with wavelength of 1.55 µm at dose from 0.10 to 2.7 J/cm2 was used.
Results. Femtosecond laser radiation in donors’ erythrocytes at specified doses was found to have no effect on the parameters of “lipid peroxidation–antioxidants” system, but dose-dependently it causes their reversible (echinocytes) and irreversible (spherocytes) transformation on the background of membrane rigidity increase. Malondialdehyde level in unchanged activity of antioxidant system enzymes increases significantly in erythrocytes of cervical cancer at Ib–IIa stage under exposure dose of 0.96–2.7 J/cm2 that can indicate an oxidative stress formation. In this respect, these doses of femtosecond laser radiation are not recommended for Ib–IIa stage cervical cancer patients.
Annually, more than 14 000 cases of cervical cancer (CC) are registered in Russia. Over 150 thousand women are being followed up after CC treatment, more than 6 000 women dying of it every year. CC morbidity rate is clearly seen to increase substantially in young women at the age of 20 to 45 years old [1]. The existing conservative methods of CC treatment are not very effective, while surgical ones (cryodestruction, electroconization, diathermocoagulation), giving rather a high percent of positive results and being widely used now, have, unfortunately, a number of essential drawbacks. The possibility of applying lasers for eliminating tumor cells is shown in several clinical and experimental works [2–4]. Coagulation necrosis, thermodestruction and evaporation of the tumor tissue are reached by using high-energy lasers with a great power radiation. Femtosecond laser radiation is also used for photodynamic tumor therapy. In this case, tumor cells are labeled with nanoparticles, gold nanorods in particular [5–7].
Femtosecond lasers are an ideal instrument for controlling processes in biological systems. Short pulse duration (about 100·10–15 s), a high peak (6 kW) and low mean (1.25 mW) power, a high time and space coherence suggest absence of marked thermal effects. Cancer cell death by apoptosis-like mechanism, excluding the development of chain radical toxic reactions, is considered to be possible [4, 8].
The above-mentioned characteristics enable researchers to apply femtosecond laser radiation (FSLI) in the preoperational period of treating large malignant tumors with a considerable decrease of radiation load on the patient and the potential of the tumor to metastasizing. However, destruction of the cancer cells by this way may cause the development of toxic reactions at the organism level [8–10]. From this point of view, the study of FSLI application in CC (Ib–IIa stage), when surgical treatment is used, may be of interest.
The aim of investigation was to assess morphofunctional condition of peripheral blood erythrocytes in the cervical cancer patients at Ib-IIa stage of the disease after femtosecond laser radiation exposure with different energy-flux density.
Materials and Methods. The objects of investigation were erythrocytes of peripheral blood from donors and CC patients, undergone examination in the Gynecological Department of Ulyanovsk Regional Clinical Oncologic Dispensary, and which had Ib–IIa stage of the disease according to FIGO (locally-limited process).
The investigation was carried out according to Helsinki Declaration (adopted in June 1964 (Helsinki, Finland) and revised in October 2000 (Edinburgh, Scotland)). All patients gave written informed consent for the scientific analysis of their data.
Radiation of erythrocytes was performed in plastic cuvettes with femtosecond laser, which is a joint development of the Scientific Center of Fiber Optics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Ulyanovsk State University (pulse duration — 100 fs; mean power — 1.25 mW; peak power — 6 kW). Four different time modes (1, 3, 5, 10 min) were used at a distance of 3 and 5 cm during radiation. The radiation doses applied were 0.10; 0.27; 0.29; 0.48; 0.81; 0.97; 1.35; 2,7 J/cm2.
To assess the topography and rigidity of erythrocytes a scanning probe microscope SolverProNT-MDT (Zelenograd, Russia) and original silicon probes with rigidity 0.20 N/m were used. Probe point curving radius was about 50 nm.
To estimate the values of “lipid peroxidation–antioxidants” system (LP–AO) in erythrocytes the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the test with thiobarbituric acid was determined, as well as enzyme activity of antioxidant protection system (APS): catalase, glutathione-S-transferase (GT), superoxide dismutase (SOD).
Statistical significance of the results obtained was assessed using nonparametric Mann–Whitny criterion. Differences between the groups were considered significant at p<0.05.
Results and Discussion. The investigation performed showed, that MDA level — a secondary product of LP — in erythrocytes of CC patients was essentially and significantly higher compared to its level in donors. After FSLI, statistically significant increase of MDA level was observed at exposure doses of 0.96; 1.35 and 2.70 J/cm2 (Table 1).
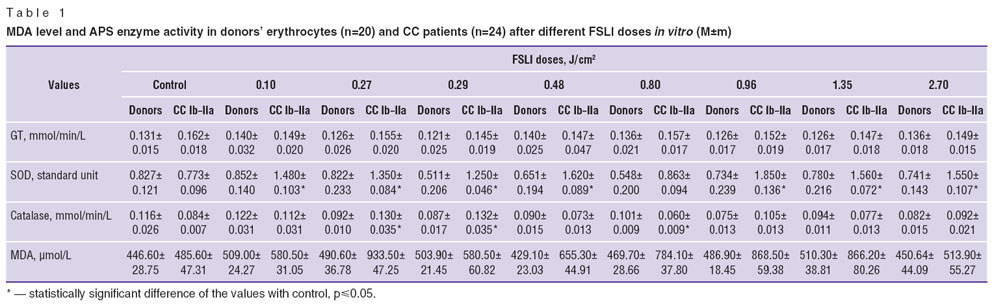 Table 1. MDA level and APS enzyme activity in donors’ erythrocytes (n=20) and CC patients (n=24) after different FSLI doses in vitro (M±m) Table 1. MDA level and APS enzyme activity in donors’ erythrocytes (n=20) and CC patients (n=24) after different FSLI doses in vitro (M±m)
|
When analyzing antioxidant enzyme activity, it was determined, that catalase activity reduced in erythrocytes of CC patients with Ib-IIa stage of the disease in comparison with the donors, grew statistically significantly under the effect of FSLI at irradiation doses of 0.27 and 0.29 J/cm2 and decreased at 0.80 J/cm2. And if simultaneous elevation of MDA level and enzyme activity of APS may testify to the transition of LP–AO system to a higher level of functioning, differently-directed dynamics of these parameters speaks about the possibility of oxidative stress development [11]. GT activity did not change significantly in erythrocytes of CC patients with Ib–IIa stage after all radiation doses, while SOD activity appeared to be significantly elevated after all FSLI doses studied, except for the dose of 0.80 J/cm2 (See Table 1).
Since 1990-s a scanning probe microscopy (SPM) technique has been actively used in biomedical investigations, enabling the scientists to study cell parameters without long and complicated fixation, and therefore, with minimum distortion of the information obtained. The SPM technique makes it possible to measure local resilient properties of cell surfaces. In the works of L.V. Korsi et al. [12] it is shown, that when erythrocytes are irradiated by semiconductor lasers, dye lasers and solid titanium-sapphire laser in different spectral ranges, deformity of erythrocytes is of resonance character depending on the bands of molecular oxygen absorption spectrum under a high pressure.
Changes of donor erythrocyte cytoarchitectonics after FSLI have been studied by us previously [13]. While scanning the samples of intact erythrocytes by the SPM technique, normocytes were mainly revealed. After FSLI exposure with energy-flow density 0.29 J/cm2, cytoarchitectonics of erythrocytes is changed. Reversibly deformed forms — echinocytes — appear on the scan. In the physiological conditions their appearance is associated with the changes of ion permeability of the membrane with the impairment of channel work. At the doses of 0.80 and 0.96 J/cm2 spherocytes appear, that is clearly seen on the 3D image. Practically all erythrocytes on the scanned samples exposed to the doses of 1.35 and 2.70 J/cm2 are spherocytes. They may be of irregular forms with altered linear dimensions.
In the course of investigation of erythrocyte architectonics of CC patients with Ib–IIa stage of the disease transformed forms are found. And transformation index (the ratio of transformed forms to discocyte number) in these patients is 2.013±0.009 (in donors — 0.126±0.012). Thus, CC patients have a decreased content of discocytes and an elevated number of reversibly (echinocytes) and irreversibly (spherocytes) transformed erythrocytes. The rise of the transformation index in CC is the result of erythrocyte increase with the extension of echinocytic row (2nd and 3rd classes), and also because of the growth of erythrocytes with the irreversibly transformed forms, stomatocytes, in particular (6th class), and erythrocytes in the form of “deflated ball” (9th class) (Fig. 1).
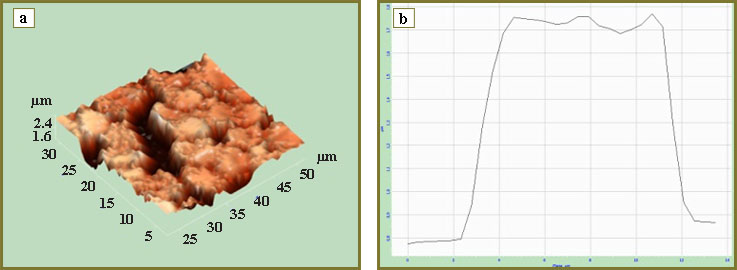 Fig. 1. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib–IIa stage of cervical cancer Fig. 1. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib–IIa stage of cervical cancer
|
Erythrocyte damage is known to augment oxidative stress [14], as transformed erythrocytes became a source of free iron (nonprotein-bound iron), which is an active oxidizing agent and is able to generate active forms of oxygen. Essential changes of erythrocytes in comparison with donors (Table 2) were estimated in CC patients with Ib–IIa stage of the disease after different doses of FSLI in the course of studies of erythrocyte architectonics. After FSLI, the number of altered forms grows with the dose increase (Fig. 2, 3).
Table 2. Morphological forms of erythrocytes in donors and CC patients (M±m) 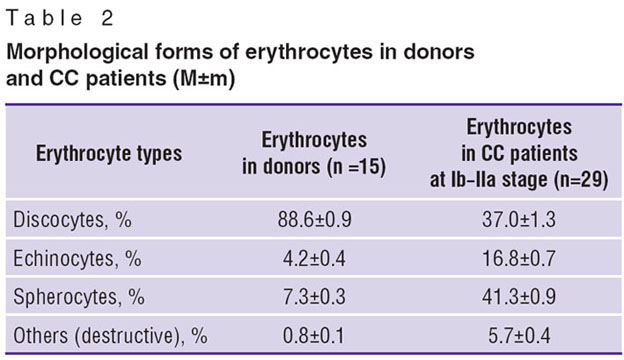
|
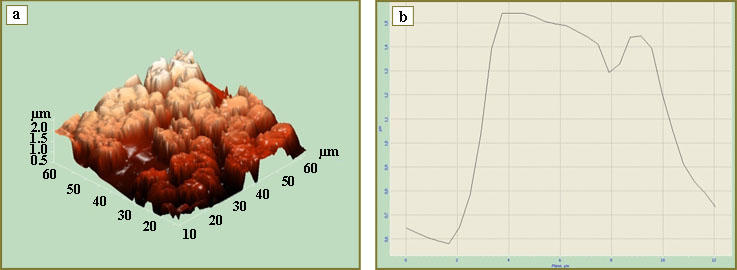 Fig. 2. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib–IIa stage of cervical cancer after the exposure to femtosecond laser radiation with the dose of 0.96 J/cm2 Fig. 2. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib–IIa stage of cervical cancer after the exposure to femtosecond laser radiation with the dose of 0.96 J/cm2
|
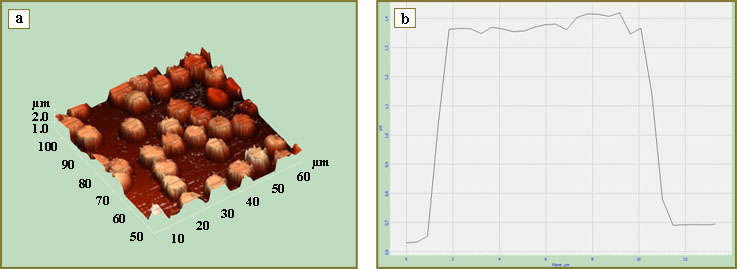 Fig. 3. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib-IIa stage of cervical cancer after the exposure to femtosecond laser radiation with the dose of 1.35 J/cm2 Fig. 3. 3D image (a) and lateral section of erythrocyte profile (b) at Ib-IIa stage of cervical cancer after the exposure to femtosecond laser radiation with the dose of 1.35 J/cm2
|
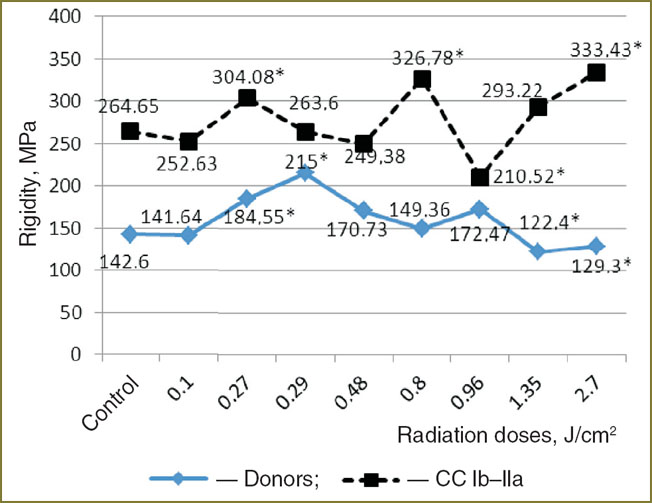
The conducted investigations showed, that FSLI effects the rigidity of erythrocyte membranes (Fig. 4), which are a very convenient object for studying oxidative stress action on cell membranes [15]. At Ib–IIa stage of CC it results in the increase of erythrocyte membrane rigidity under the exposure to all the doses studied, except for the dose of 0.96 J/cm2. While irradiation of donors’ erythrocytes at energy-flow densities of 1.35 and 2.7 J/cm2 causes reduction of membrane rigidity (See Fig. 4).
Thus, in patients with CC (Ib–IIa stage) at FSLI doses of 0.96–2.7 J/cm2 an oxidative stress may occur in case of no significant changes in cytoarchitectonics of erythrocytes.
Conclusion. Femtosecond laser radiation at specified doses of 0.10–2.7 J/cm2 in donors’ erythrocytes does not influence the parameters of “lipid peroxidation–antioxidants” system, but dose-dependently causes their reversible (echinocytes) and irreversible (spherocytes) transformation together with the increase of membrane rigidity. In erythrocytes of patients having cervical cancer at Ib–IIa stage the level of malondialdehyde rises significantly at the radiation doses of 0.96–2.7 J/cm2 under unchanged enzyme activity of the antioxidant system, that may speak of the development of an oxidative stress.
Study Funding. This work was funded by the State Task of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation.
Conflict of Interests. The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
References
- Chissov V.I., Starinskiy V.V., Petrova G.V. Zlokachestvennye novoobrazovaniya v Rossii v 2009 godu (zabolevaemost’ i smertnost’) [Malignant neoplasms in Russia in 2009 (incidence and death rate)]. Moscow; 2011; 260 p.
- Cheremisina O.V., Vusik M.V., Soldatov A.N., Reiner I.B. Sovremennye vozmozhnosti endoskopicheskikh lazernykh tekhnologiy v klinicheskoy onkologii [Endoscopic laser technologies in clinical oncology]. Sibirskiy onkologicheskiy zhurnal — Siberian Journal of Oncology 2007; 4: 5–11.
- Castren-Persons M., Schr?der T., Lehtonen E. Sensitivity to Nd:YAG induced laserthermia is a cell-type-specific feature not directly related to tumorigenic potential or proliferation rate. Lasers Surg Med 1996; 18(4): 420–428.
- Anguez F.A., Courtade E., Silvery A., Suret P., Randoux S. A high-power tunable Raman fiber ring for the investigation of singlet oxygen production from direct laser excitation around 1270 nm. Optics Express 2010; 18(22): 22928–22936, http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.022928.
- Tse C., Zohdy M.J., Ye J.Y., O`Donnell M., Lesniak W., Balogh L. Enhanced optical breakdown in KB cells labeled with folate-targeted silver-dendrimer composite nanodevices. Nanomedicine 2011; 7(1): 97–106, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2010.09.003.
- Kuo T.R., Hovhannisyan V.A., Chao Y.C., Chao S.L., Chiang S.J., Lin S.J. Multiple release kinetics of targeted drug from gold nanorod embedded polyelectrolyte conjugates induced by near-infrared laser irradiation. J Am Chem Soc 2010; 132(40): 14163–14171, http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja105360z.
- Li J.L., Gu M. Surface plasmonic gold nanorods for enhanced two-proton microscopic imaging and apoptosis induction of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010; 31(36): 9492–9498, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.068.
- Weyergang A., Selbo P.K., Bestad M.E., Bostad M., Berg K. Photochemical internalization of tumor-targeted protein toxins. Lasers Surg Med 2011; 43(7): 721–733.
- Paiva M.B., Joo J., Abrahao M., Ribeiro J.C., Cervantes O., Sercarz J.A. Update on laser photochemotherapy: аn alternative for cancer treatment. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 2011; 9: 32–37, http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/187152011797378742.
- Moskalik K.G., Alexeeva L.N., Novik V.I., Demin E.V., Kozlov A.P. Morphological changes in human skin melanoma treated by high-energy pulsed neodymium laser radiation. J BUON 2011; 16(2): 341–344.
- Lyu B.N., Lyu M.B., Ismailov B.I. Rol’ mitokhondriy v razvitii i regulyatsii urovnya okislitel’nogo stressa v norme, pri kletochnykh patologiyakh i reversii opukholevykh kletok [The role of mitochondria in oxidative stress development and regulation in norm, cell pathology and tumor cell reversion]. Uspekhi sovremennoy biologii — Advance of Modern Biology 2006; 126(4): 388–398.
- Korsi L.V., Sokolov V.G. Laser method of photochemical destruction of tumors without exogenetic sensitizers. In: Laser optical systems and technologies. Federal state unitary enterprise NPO astrophysics. M; 2009: 101–106.
- Signorini C., Perrone S., Sgherri C., Ciccoli L., Buonocore G., Leoncini S. Plasma esterified F2-isoprostanes and oxidative stress in newborns: role of nonprotein-bound iron. Pediatr Res 2008; 63(3): 287–291, http://dx.doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318163a1fd.
- Gening T.P., Arslanova D.R., Abakumova T.V., Svetukhin V.V., Antoneeva I.I., Gening S.O. Morfofunktsional’noe sostoyanie eritrotsitov perifericheskoy krovi posle vozdeystviya femtosekundnogo lazernogo izlucheniya [Morphofunctional state of peripheral blood erythrocytes after femtosecond laser treatment]. Sovrem Tehnol Med — Modern Technologies in Medicine 2013; 5(1): 58–63.
- Tsuda K. Oxidative stress and membrane fluidity of red blood cells in hypertensive and normotensive men: an electron spin resonance investigation. Int Heart J 2010; 51(2): 121–124, http://dx.doi.org/10.1536/ihj.51.121.