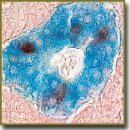
Distribution of S100-Positive Cells in Islets of Langerhans of the Fetal and Adult Human Pancreas
The aim of the investigation was to study the distribution of S100-positive cells in the islets of Langerhans of human pancreas during prenatal and early postnatal development, as well as in adult humans.
Materials and Methods. Using antibodies to S100 protein, to main hormones produced in the islets of Langerhans in human pancreas (insulin, glucagon and somatostatin), and to neuron-specific enolase (NSE) we carried out an immunohistochemical analysis of human pancreatic samples. The samples were taken from adults without pancreatic diseases, from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, as well as from fetuses and newborns.
Results. Two types of S100-positive cells can be found in human islets of Langerhans starting from gestation week 15–16: cells located on islet periphery, and cells situated inside an islet. Cells located on periphery are flattened and have small amount of cytoplasm. These cells have long processes extending mainly along periphery. The cells located inside islets are oval- or round-shaped, and generally have no processes.
Conclusion. In an early fetal period in islets of Langerhans of human pancreas, two types of S100-positive cells appear, they being different in their structure. The cells on periphery are similar morphologically to glial cells. The cells inside islets are no different in their structure from other endocrine cells. Two types of S100-positive cells can be suggested to be of importance both in islet morphology, and in the regulation of hormones expressed by endocrine cells.
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6-th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2013; 159 p.
- Dedov I.I., Balabolkin M.I., Klebanova E.M. Modern aspects of pancreatic islet transplantation in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus 2004; 2: 34–41.
- Scheen A.J. Diabetes mellitus in the elderly: insulin resistance and/or impaired insulin secretion? Diabetes & Metabolism 2005; 31(1): 5S27–5S34, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1262-3636(05)73649-1.
- Wierup N., Svensson H., Mulder H., Sundler F. The ghrelin cell: a novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul Pept 2002; 107(1–3): 63–69, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-0115(02)00067-8.
- Wierup N., Sundler F., Heller R.S. The islet ghrelin cell. J Mol Endocrinol 2013; 52(1): R35–R49, http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/jme-13-0122.
- Lászik Z., Krenács T., Dobó E. S-100 protein immunoreactivity in human islets of Langerhans. Acta Morphol Hung 1989; 37(1–2): 117–124.
- Takayanagi M., Watanabe T. Immunocytochemical colocalizations of insulin, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, dopamine beta-hydroxylase, S-100 protein and chromogranin A in B-cells of the chicken endocrine pancreas. Tissue Cell 1996; 28(1): 17–24, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0040-8166(96)80040-1.
- Uchida T., Endo T. Identification of cell types containing S-100b protein-like immunoreactivity in the islets of Langerhans of the guinea pig pancreas with light and electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 1989; 255(2): 379–384, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf00224121.
- Sunami E., Kanazawa H., Hashizume H., Takeda M., Hatakeyama K., Ushiki T. Morphological characteristics of Schwann cells in the islets of Langerhans of the murine pancreas. Arch Histol Cytol 2001; 64(2): 191–201, http://doi.org/10.1679/aohc.64.191.
- Girod C., Durand N., Raccurt M. Immunostaining of a cell type in the islets of Langerhans of the monkey Macaca irus by antibodies against S-100 protein. Cell Tissue Res 1987; 247(1): 11–16, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf00216541.
- Fujita T. Histological studies on the neuro-insular complex in the pancreas of some mammals. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 1959; 50: 94–109, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf00342656.
- Proshchina A.E., Krivova Y.S., Barabanov V.M., Saveliev S.V. Ontogeny of neuro-insular complexes and islets innervation in the human pancreas. Front Endocrinol 2014; 5: 57, http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00057.
- Donato R., Cannon B.R., Sorci G., Riuzzi F., Hsu K., Weber D.Y., Geczy C.L. Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol Med 2013; 13(1): 24–57, http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1566524011307010024.
- Donato R., Sorci G., Riuzzi F., Arcuri C., Bianchi R., Brozzi F., Tubaro C., Giambanco I. S100B’s double life: intracellular regulator and extracellular signal. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793(6): 1008–1022, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.11.009.
- Fujita T., Iwanaga T., Nakajima T. Immunohistochemical detection of nervous system-specific proteins in normal and neoplastic paraneurons in the gut and pancreas. In: Gut peptides and ulcer. Miyoshi A. (editor). Tokyo: Biomedical Research Foundation; 1983; p. 81–88.
- Proshchina A.E., Savel’yev S.V. Immunohistochemical study of α- and β-cell distribution in human pancreatic Langerhans islets of various types. Bull Exp Biol Med 2013; 155(6): 798–801, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10517-013-2255-5.
- Jeon J., Correa-Medina M., Ricordi C., Edlund H., Diez J.A. Endocrine cell clustering during human pancreas development. J Histochem Cytochem 2009; 57(9): 811–824, http://dx.doi.org/10.1369/jhc.2009.953307.
- De Krijger R.R., Aanstoot H.J., Kranenburg G., Reinhard M., Visser W.J., Bruining G.J. The midgestational human fetal pancreas contains cells coexpressing islet hormones. Dev Biol 1992; 153(2): 368–375, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0012-1606(92)90121-V.
- Piper K., Brickwood S., Turnpenny L.W., Cameron I.T., Ball S.G., Wilson D.I., Hanley N.A. Beta cell differentiation during early human pancreas development. J Endocrinol 2004; 181(1): 11–23, http://dx.doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1810011.
- Meier J.J., Köhler C.U., Alkhatib B., Sergi C., Junker T., Klein H.H., Schmidt W.E., Fritsch H. Beta-cell development and turnover during prenatal life in humans. Eur J Endocrinol 2010; 162(3): 559–568, http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/EJE-09-1053.
- Squires P.E., Jones P.M., Younis M.Y., Hills C.E. The calcium-sensing receptor and β-cell function. Vitam Horm 2014; 95: 249–267, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00010-7.










