Contribution of Laser-Induced Gas-Vapor-Liquid Dynamics to the Mechanism of Endovenous Laser Ablation
The aim of the investigation is to ground experimentally the mechanism of endovenous laser ablation (EVLA), based on laser-induced convective heat transfer from the blood to the vein walls due to its boiling as a dominating process in a complicated mechanism of heat exchange occurring in endovasal laser manipulations.
Materials and Methods. In experimental modeling of EVLA, fragments of varicose trunks of great suphenous veins, removed by combined phlebectomy, have been used. Laser radiation with 970 nm wavelength and 6 and 7 W power was delivered into the vein through a quartz optical fiber with a flat preblackened (initiated) tip. Pullback velocity was 0.5 mm/s. The surface temperature of the vein was measured during laser radiation using FLIR A600 (Sweden) infrared camera. Denaturation of collagen in the vein wall caused by laser impact was determined by differential scanning calorimetry.
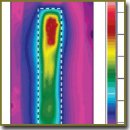
Results. Recording the surface temperature dynamics of vein with infrared camera allowed visualization of spot heating of the vein wall by the fluid surrounding the gas-steam bubbles. Temperature saturation in the dynamics of heating the media under study has been established to exist, being one of the characteristic features of the first-order phase transition. The degree of collagen denaturation in the venous wall specimens at 6 and 7 W amounted to 87±5 and 97±3%, respectively.
Conclusion. Bubble boiling of blood in the veins, providing fast and efficient heat transfer from the heated tip of the quartz optical fiber to the vein walls, has been experimentally confirmed. For successful performing of the EVLA, the fiber traction must be started at the moment of blood boiling; at lower laser powers the fiber must be held for a longer period. In clinical EVLA procedures less powerful and safer laser devices can be used, reducing the risk of post-treatment complications.
- Bone Salat C. Tratamiento endoluminal de las varices con láser de diodo. Estudio preliminar. Revista de Patología Vascular 1999; 5(1): 31–39.
- Shevchenko Iu.L., Stoiko Iu.M., Mazaishvili K.V., Maksimov S.V., Tsypliashchuk A.V., Parikov M.A., Ignat’eva N.Iu., Zakharkina O.L. The choice of the optimal parameters of 1470 nm radiation for endovenous laser obliteration. Flebologiya 2013; 7(4): 18–24.
- Kutateladze S.S. Osnovy teorii teploobmena [Fundamentals of heat transfer theory]. Moscow: Atomizdat; 1979; 416 p.
- Proebstle T.M., Lehr H.A., Kargl A., Espinola-Klein C., Rother W., Bethge S., Knop J. Endovenous treatment of the greater saphenous vein with a 940-nm diode laser: thrombotic occlusion after endoluminal thermal damage by laser-generated steam bubbles. J Vasc Surg 2002; 35(4): 729–736, http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mva.2002.121132.
- Proebstle T., Sandhofer M., Kargl A., Gül D., Rother W., Knop J., Lehr H.A. Thermal damage of the inner vein wall during endovenous laser treatment: key role of energy absorption by intravascular blood. Dermatol Surg 2002; 28(7): 596–600, http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01309.x.
- van der Geld C.W., van den Bos R.R., van Ruijven P.W., Nijsten T., Neumann H.A., van Gemert M.J. The heat-pipe resembling action of boiling bubbles in endovenous laser ablation. Lasers Med Sci 2010; 25(6): 907–909, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10103-010-0780-2.
- Malskat W.S., Poluektova A.A., van der Geld C.W., Neumann H.A., Weiss R.A., Bruijninckx C.M., van Gemert M.J. Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA): a review of mechanisms, modeling outcomes, and issues for debate. Lasers Med Sci 2014; 29(2): 393–403, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1480-5.
- Shevchenko Iu.L., Stoiko Iu.M., Mazaishvili K.V., Khlevtova T.V. Mechanism of endovasal laser obliteration: a novel view. Flebologiya 2011; 5(1): 46–50.
- Zhilin K.M. Vliyanie dliny volny lazernogo izlucheniya blizhnego IK-diapazona na kharakter silovogo vozdeystviya na biologicheskie tkani (krov', venoznaya stenka, slizistaya obolochka i kostnaya tkan'). Avtoref. dis. ... kand. fiz.-mat. nauk [Effect of the wavelength of near IR-range laser radiation to the character of force action on biological tissues (blood, venous wall, mucous membrane and bone tissue). PhD Thesis]. Moscow; 2013.
- Roggan A., Friebel M., Dörschel K., Hahn A., Müller G. Optical properties of circulating human blood in the wavelength range 400–2500 nm. J Biomed Opt 1999; 4(1): 36–46, http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.429919.
- Proebstle T.M., Gül D., Kargl A., Knop J. Endovenous laser treatment of the lesser saphenous vein with a 940-nm diode laser: early results. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29(4): 357–361, http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29085.x.
- Oh C.K., Jung D.S., Jang H.S., Kwon K.S. Endovenous laser surgery of the incompetent greater saphenous vein with a 980-nm diode laser. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29(11): 1135–1140, http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29353.x.
- Weiss R.A. Comparison of endovenous radiofrequency versus 810 nm diode laser occlusion of large veins in an animal model. Dermatol Surg 2002; 28(1): 56–61, http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01191.x.
- Schwarz T., von Hodenberg E., Furtwängler C., Rastan A., Zeller T., Neumann F.J. Endovenous laser ablation of varicose veins with the 1470-nm diode laser. J Vasc Surg 2010; 51(6): 1474–1478, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2010.01.027.
- Rathod J., Taori K., Joshi M., Mundhada R., Rewatkar A., Dhomane S., Gour P. Outcomes using a 1470-nm laser for symptomatic varicose veins. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2010; 21(12): 1835–1840, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2010.09.009.
- Sokolov A.L., Liadov K.V., Lutsenko M.M., Lavrenko S.V., Liubimova A.A., Verbitskaya G.O., Minaev V.P. Endovascular laser ablation with wavelength 1.56 nm for varicose veins. Angiologiya i sosudistaya khirurgiya 2009; 15(1): 69–76.
- Shaidakov E.V., Iliukhin E.A., Petukhov A.V., Rosukhovskii D.A. Comparison of lasers emitting at 970 and 1470 nm wavelengths for the in vitro simulation of endovasal laser vein obliteration. Flebologiya 2011; 5(4): 23–30.
- Amzayyb M., van den Bos R.R., Kodach V.M., de Bruin D.M., Nijsten T., Neumann H.A., van Gemert M.J. Carbonized blood deposited on fibres during 810, 940 and 1470 nm endovenous laser ablation: thickness and absorption by optical coherence tomography. Lasers Med Sci 2010; 25: 439–447, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0749-1.
- Mordon S., Wassmer B., Servell P., Desmyttère J., Grard C., Stalnikiewicz G. Is a vein filled with blood a good model for studying endovenous laser ablation? Lasers Surg Med 2009; 41(8): 543–544, http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20809.
- van den Bos R.R., Kockaert M.A., Martino Neumann H.A., Bremmer R.H., Nijsten T., van Gemert M.J. Heat conduction from the exceedingly hot fiber tip contributes to the endovenous laser ablation of varicose veins. Lasers Med Sci 2009; 24(2): 247–251, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10103-008-0639-y.
- Yusupov V.I., Chudnovskii V.M., Bagratashvili V.N. Laser-induced hydrodynamics in water-saturated biotissues. 1. Generation of bubbles in liquid. Laser Phys 2010; 20(7): 1641–1647, http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X1014001X.
- Yusupov V.I., Chudnovskii V.M., Bagratashvili V.N. Laser-induced hydrodynamics in water-saturated biotissues: 2. Effect on delivery fiber. Laser Phys 2011; 21(7): 1230–1234, http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X11140015.
- Yusupov V.I., Chudnovskii V.M., Bagratashvili V.N. Laser-induced hydrodynamics in water and biotissues nearby optical fiber tip. In: Hydrodynamics — advanced topics. Schulz H.E. (editor). InTech; 2011; p. 95–118, http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/28517.
- Chudnovskii V.M., Yusupov V.I. Punktsionnaya svetovodnaya igla (varianty) i ogranichitel’ dlya nee [Puncture optical fiber needle (variants) and a limiter for it]. Patent PF 58904. 2006.
- Shevchenko Yu.L., Stoyko Yu.M., Mazayshvili K.V. Lazernaya khirurgiya varikoznoy bolezni [Laser surgery of varicose disease]. Moscow: Borges; 2010.
- Dexter D., Kabnick L., Berland T., Jacobowitz G., Lamparello P., Maldonado T., Mussa F., Rockman C., Sadek M., Giammaria L.E., Adelman M. Complications of endovenous lasers. Phlebology 2012; 27(Suppl 1): 40–45, http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/phleb.2012.012S18.
- Dunst K.M., Huemer G.M., Wayand W., Shamiyeh A. Diffuse phlegmonous phlebitis after endovenous laser treatment of the greater saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg 2006; 43(5): 1056–1058, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2006.01.030.
- Chudnovskyi V., Bulanov V., Jusypov V. Laser induction of acoustic hydrodynamical effects in medicine. Fotonika 2010; 1: 30–36.
- Chudnovsky V.M., Yusupov V.I., Machovskaya T.G. Laser-induced acustohydrodynamic effects in surgery of disc hernia. Vestnik nevrologii, psikhiatrii i neyrokhirurgii 2013; 4: 76–82.
- Kuchareva L.I., Nevouzhai V.I., Chudnovsky V.M. Tltrasonography in diagnostics and sclerotizing therapy of cyst formation of the breasts. Dal'nevostochnyy meditsinskiy zhurnal 2008; 3: 49–51.
- Yusupov V.I., Bulanov V.V., Chudnovskii V.M., Bagratashvili V.N. Laser-induced hydrodynamics in water-saturated tissue: III. Optoacoustic effects. Laser Phys 2014; 24(1), http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1054-660X/24/1/015601.
- Willett T.L., Labow R.S., Lee J.M. Mechanical overload decreases the thermal stability of collagen in an in vitro tensile overload tendon model. J Orthop Res 2008; 26(12): 1605–1610, http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jor.20672.
- Ignat'eva N.Yu. Termicheskaya stabil'nost' kollagena v soedinitel'nykh tkanyakh. Avtoref. dis. ... dokt. khim. nauk [Thermal stability of collagen in connective tissues. PhD Thesis]. Moscow; 2011.
- van der Geld C.W.M. The dynamics of a boiling bubble before and after detachment. Heat Mass Transf 2009; 45(7): 831–846, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00231-007-0254-7.










