Multiphoton Microscopy in the Study of Morphological Characteristics of Radiation-Induced Injuries of the Bladder
The aim of the investigation was to assess the feasibility of multiphoton microscopy (MPM) for studying dynamics of bladder structural changes following a single exposure to gamma-radiation at various doses (2, 10, and 40 Gy) in experiment.
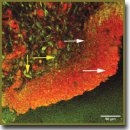
Materials and Methods. Specimens of rat bladders after a single local radiation at the dose of 2, 10, and 40 Gy were the objects of investigation (9 groups with two rats for each dose and term, and two intact rats — 20 observations in all). The study was carried out 1 day, 1 week, and 1 month after radiation exposure. Part of the histological bladder preparations was stained with picrofuchsin according to Van Gieson method. The other part of the sections, obtained from the same blocks, was investigated using MPM without additional staining. For this purpose a laser scanning microscope LSM Axiovert 510 Meta (Carl Zeiss, Germany) was used. Excitation was generated with a femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser (MAI TAI HP, Spectra Physics, USA) at the wavelength of 800 nm, registration was performed in the range of 362–415 nm (second harmonic signal from collagen) and 512–576 nm (signal of two-photon excited elastin autofluorescence).
Results. Application of MPM method allowed us to find out, that in early terms (1 day and 1 week) after radiation exposure the process of alteration of collagen-containing structures of bladder walls was a leading one at all selected doses. A month after 2 and 10 Gy radiation increase in collagen structures was registered, speaking of the onset of radiation fibrosis formation. At a dose of 40 Gy decrease of second harmonic signal retained in the extracellular matrix of the bladder wall. It allowed us to draw a conclusion on a long-term disorganization of collagen at high radiation doses.
Conclusion. MPM method makes it possible to estimate, that structural destruction of extracellular tissue matrix occurs even after low radiation doses and in early terms after radiation exposure, which is not possible to reveal using standard microscopy. Duration of disorganization process of collagen-containing structures depends on the radiation dose: high doses result in longer-lasting alterations. MPM enables also the assessment of the course of restorative processes.
- Dörr W. Radiation effect in normal tissue — principles of damage and protection. Nuklearmedizin 2010; 49(Suppl 1): S53–S58.
- Fiorino C., Valdagni R., Rancati T., Sanguineti G. Dose-volume effects for normal tissues in external radiotherapy: pelvis. Radiother Oncol 2009; 93(2): 153–167, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2009.08.004.
- Yarnold J., Brotons M.C.V. Pathogenetic mechanisms in radiation fibrosis. Radiother Oncol 2010; 97(1): 149–161, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.09.002.
- Stewart F.A., Akleyev A.V., Hauer-Jensen M., Hendry J.H., Kleiman N.J., Macvittie T.J., Aleman B.M., Edgar A.B., Mabuchi K., Muirhead C.R., Shore R.E., Wallace W.H. ICRP publication 118: ICRP statement on tissue reactions and early and late effects of radiation in normal tissues and organs — threshold doses for tissue reactions in a radiation protection context. Ann ICRP 2012; 41(1–2): 1–322, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.icrp.2012.02.001.
- Brush J., Lipnick S.L., Phillips T., Sitko J., McDonald J.T., McBride W.H. Molecular mechanisms of late normal tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol 2007; 17(2): 121–130, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2006.11.008.
- Maslennikova A., Kochueva M., Ignatieva N., Vitkin A., Zakharkina O., Kamensky V., Sergeeva E., Kiseleva E., Bagratashvili V. Effects of gamma irradiation on collagen damage and remodeling. Int J Radiat Biol 2015; 91(3): 240–247, http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09553002.2014.969848.
- Göppert-Mayer M. Über elementarakte mit zwei quantensprüngen. Ann Phys 1931; 401(3): 273–295, http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/andp.19314010303.
- Alex A., Weingast J., Weinigel M., Kellner-Höfer M., Nemecek R., Binder M., Pehamberger H., König K., Drexler W. Three-dimensional multiphoton/optical coherence tomography for diagnostic applications in dermatology. J Biophotonics 2013; 6(4): 352–362, http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201200085.
- Denk W., Strickler J.H., Webb W.W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 1990; 248(4951): 73–76, http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.2321027.
- Theodossiou T.A., Thrasivoulou C., Ekwobi C., Becker D.L. Second harmonic generation confocal microscopy of collagen type I from rat tendon cryosections. Biophys J 2006; 91(12): 4665–4677, http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.093740.
- Seidenari S., Arginelli F., Bassoli S., Cautela J., French P.M., Guanti M., Guardoli D., König K., Talbot C., Dunsby C. Multiphoton laser microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging for the evaluation of the skin. Dermatol Res Pract 2012; 2012: 810749, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/810749.
- Williams R.M., Zipfel W.R., Webb W.W. Interpreting second-harmonic generation images of collagen I fibrils. Biophys J 2005; 88(2): 1377–1386, http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.047308.
- Raub C.B., Unruh J., Suresh V., Krasieva T., Lindmo T., Gratton E., Tromberg B.J., George S.C. Image correlation spectroscopy of multiphoton images correlates with collagen mechanical properties. Biophys J 2008; 94(6): 2361–2373, http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.120006.
- Chen J., Wong S., Nathanson M.H., Jain D. Evaluation of Barrett esophagus by multiphoton microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014; 138(2): 204–212, http://dx.doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2012-0675-OA.
- Dimitrow E., Ziemer M., Koehler M.J., Norgauer J., König K., Elsner P., Kaatz M. Sensitivity and specificity of multiphoton laser tomography for in vivo and ex vivo diagnosis of malignant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129(7): 1752–1758, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.439.
- Balu M., Kelly K.M., Zachary C.B., Harris R.M., Krasieva T.B., König K., Durkin A.J., Tromberg B.J. Distinguishing between benign and malignant melanocytic nevi by in vivo multiphoton microscopy. Cancer Res 2014; 74(10): 2688–2697, http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2582.
- Huang A.S., Gonzalez J.M. Jr., Le P.V., Heur M., Tan J.C. Sources of structural autofluorescence in the human trabecular meshwork. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54(7): 4813–4820, http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-11235.
- Morishige N., Yamada N., Zhang X., Morita Y., Yamada N., Kimura K., Takahara A., Sonoda K.H. Abnormalities of stromal structure in the bullous keratopathy cornea identified by second harmonic generation imaging microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53(8): 4998–5003, http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-10214.
- Koehler M.J., König K., Elsner P., Bückle R., Kaatz M. In vivo assessment of human skin aging by multiphoton laser scanning tomography. Opt Lett 2006; 31(19): 2879–2881, http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/ol.31.002879.
- Tsai T.H., Jee S.H., Dong C.Y., Lin S.J. Multiphoton microscopy in dermatological imaging. J Dermatol Sci 2009; 56(1): 1–8, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.06.008.
- Cicchi R., Matthäus C., Meyer T., Lattermann A., Dietzek B., Brehm B.R., Popp J., Pavone F.S. Non-linear imaging and characterization of atherosclerotic arterial tissue using combined two photon fluorescence, second-harmonic generation and CARS microscopy. Proc. SPIE 8948, Multiphoton Microscopy in the Biomedical Sciences XIV, 894807 (February 28, 2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.203701822.
- Chen W.S., Wang Y., Liu N.R., Zhang J.X., Chen R. Multiphoton microscopic imaging of human normal and cancerous oesophagus tissue. J Microsc 2014; 253(1): 79–82, http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12102.
- Paoli J., Smedh M., Ericson M.B. Multiphoton laser scanning microscopy — a novel diagnostic method for superficial skin cancers. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2009; 28(3): 190–195, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sder.2009.06.007.
- Burke K., Tang P., Brown E. Second harmonic generation reveals matrix alterations during breast tumor progression. J Biomed Opt 2012; 18(3): 031106, http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.18.3.031106.
- Campagnola P. Second harmonic generation imaging microscopy: applications to diseases diagnostics. Anal Chem 2011; 83(9): 3224–3231, http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ac1032325.
- Yasui T., Tanaka R., Hase E., Fukushima Sh., Araki T. In vivo time-laps imaging of skin-burn wound healing using second-harmonic generation microscopy. Proc. SPIE 8948, Multiphoton Microscopy in the Biomedical Sciences XIV, 89480B (February 28, 2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.2038022.
- Kiseleva E., Kirillin M., Feldchtein F., Vitkin A., Sergeeva E., Zagaynova E., Streltzova O., Shakhov B., Gubarkova E., Gladkova N. Differential diagnosis of human bladder mucosa pathologies in vivo with cross-polarization optical coherence tomography. Biomed Opt Express 2015; 6(4): 1464–1476, http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/BOE.6.001464.










