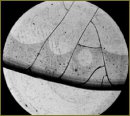
Crystallogenic Properties of a Biological Fluid in Chemical Agent Infusion
There have been studied cocrystallization peculiarities of blood serum with urea water solutions of different concentration (30; 15; 7.5; 3.75 and 1.725%) in the ratio 1:1 compared to a proper structure-forming biosubstrate considering the uremia initial level. The urea dose-dependent infusion has been stated to alter the crystallogenic properties of biological fluid up to a full suppression of its proper crystallization in high concentrations of the compound (15 and 30% solutions), however, the shift expression is determined by initial endogenous urea content in blood.










