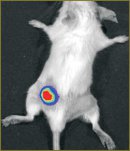
In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging of Tumor Cells Using Optimized Firefly Luciferase luc2
The present study was aimed to establish a tumor cell line stably expressing luciferase luc2, and to develop the technique to observe primary tumor nodes and metastases using in vivo bioluminescence imaging.
Materials and Methods. In this research we used pLuc2-N plasmid, lentiviral vector pLVT-1, Colo 26 cell line and BALB/c mice to generate new bioluminescent tumor model. Bioluminescence imaging in vitro и in vivo was carried out on IVIS-Spectrum system (Caliper Life Sciences, USA). Primary tumor model was created by subcutaneous injection of 500 000 Colo 26-luc2 cells. Model of metastases was generated by i.v. injection of 75 000 Colo 26-luc2 cells. Histological analysis was performed to verify the results of the imaging.
Results. We created the lentiviral vector containing luc2 gene using molecular cloning. Then Colo 26-luc2 tumor cell line was generated. We assessed the sensitivity of luc2-based bioluminescence imaging. The intensity of bioluminescent signal in vitro averaged about 5000 photon/s per cell, in vivo — 250 photon/sec per cell. In vivo monitoring of Colo 26-luc2 primary tumor and metastases was demonstrated. The results of bioluminescence imaging correlated with histological analysis data.
Conclusion. The present work shows the possibility of bioluminescent system based on optimized luciferase luc2 for in vivo noninvasive high-sensitive whole-body imaging of tumors.
- Luker G.D., Luker K.E. Optical imaging: current applications and future directions. J Nucl Med 2008; 49(1): 1–4.
- Close D.M., Patterson S.S., Ripp S., Baek S.J., Sanseverino J., Sayler G.S. Autonomous bioluminescent expression of the bacterial luciferase gene cassette (lux) in a mammalian cell line. PLoS One 2010; 5(8): 12441.
- Greer L.F. 3rd, Szalay A.A. Imaging of light emission from the expression of luciferases in living cells and organisms: a review. Luminescence 2002; 17(1): 43–74.
- De Wet J.R., Wood K.V., DeLuca M., Helinski D.R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 1987; 7: 725–737.
- Conti E., Franks N.P., Brick P. Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure 1996; 4(2): 287–298.
- Paguio A., Almond B., Fan F., Stecha P., Garvin D., Wood M., et al. pGL4 vectors: а new generation of luciferase reporter vectors. Promega Notes 2005; 89: 4.
- Marques S.M., Esteves da Silva J.C. Firefly bioluminescence: a mechanistic approach of luciferase catalyzed reactions. IUBMB Life 2009; 61(1): 6–17.
- Sato A., Klaunberg B., Tolwani R. In vivo bioluminescence imaging. Comp Med 2004; 54(6): 631–634.
- Kim J.B., Urban K., Cochran E., Lee S., Ang A., Rice B., et al. Non-invasive detection of small number of bioluminescent cancer cells in vivo. PLoS One 2010; 5(2): 9364.
- Hickson J., Ackler S., Klaubert D., Bouska J., Ellis P., Foster K., et al. Noninvasive molecular imaging of apoptosis in vivo using a modified firefly luciferase substrate, Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17(6): 1003–1010.
- Paroo Z., Bollinger R.A., Braasch D.A., Richer E., Corey D.R., Antich P.P., et al. Validating bioluminescence imaging as a high-throughput, quantitative modality for assessing tumor burden. Mol Imaging 2004; 3(2): 117–124.
- Wetterwald A., van der Pluijm G., Que I., Sijmons B., Buijs J., Karperien M., et al. Optical imaging of cancer metastasis to bone marrow: a mouse model of minimal residual disease. Am J Pathol 2002; 160(3): 1143–1153.
- Jenkins D.E., Oei Y., Hornig Y.S., Yu S.F., Dusich J., Purchio T., et al. Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) to improve and refine traditional murine models of tumor growth and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 2003; 20(8): 733–744.
- Lim E., Modi K.D., Kim J. In vivo bioluminescent imaging of mammary tumors using IVIS spectrum. J Vis Exp 200; 26: 1210.
- Wang K., Xie S., Ren Y., Xia H., Zhang X., He J. Establishment of a bioluminescent MDA-MB-231 cell line for human triple-negative breast cancer research. Oncol Rep 2012; 27(6): 1981–1989.
- Kang M.R., Yang G., Charisse K., Epstein-Barash H., Manoharan M., Li L.C. An orthotopic bladder tumor model and the evaluation of intravesical saRNA treatment. J Vis Exp 2012; 28: 65.
- Henderson B.W., Gollnick S.O., Snyder J.W., Busch T.M., Kousis P.C., Cheney R.T., et al. Choice of oxygen-conserving treatment regimen determines the inflammatory response and outcome of photodynamic therapy of tumors. Cancer Res 2004; 64(6): 2120–2126.
- Golab J., Wilczynski G., Zagozdzon R., Stokіosa T., Dabrowska A., Rybczyсska J., et al. Potentiation of the anti-tumour effects of Photofrin-based photodynamic therapy by localized treatment with G-CSF. Br J Cancer 2000; 82(8): 1485–1491.
- Tsuruo T., Yamori T., Naganuma K., Tsukagoshi S., Sakurai Y. Characterization of metastatic clones derived from a metastatic variant of mouse colon adenocarcinoma 26. Cancer Res 1983; 43(11): 5437–5442.
- Klages N., Zufferey R., Trono D. A stable system for the high-titer production of multiply attenuated lentiviral vectors. Mol Ther 2000; 2: 170–176.
- Meleshina А.V., Cherkasova Е.I., Sergeeva Е.А., Kleshnin М.S., Turchin I.V., Kiseleva Е.V., Dashinimaev E.V., Shirmanova М.V., Lukyanov S.А., Zagaynova Е.V. Issledovanie vzaimodeystviya mezenkhimnykh kletok i opukholi metodami fluorestsentnogo bioimidzhinga [The study of the interaction of mesenchymal stem cells and the numor using the methods of fluorescent bioimaging]. Sovrem Tehnol Med — Modern Technologies in Medicine 2012; 4: 7–16.
- Shirmanova M.V., Snopova L.B., Prodanets N.N., Serebrovskaya Е.О., Ignatova N.I., Sergeeva Е.А., Kamensky V.А., Klementyeva N.V., Lukyanov K.А., Lukyanov S.А., Zagaynova Е.V. Patomorfologicheskoe issledovanie fototoksichnosti geneticheski-kodiruemogo fotosensibilizatora KillerRed na opukholyakh zhivotnykh [Pathomorphological study of phototoxicity of genetically-encoded photosensitizer KillerRed on animal tumors]. Sovrem Tehnol Med — Modern Technologies in Medicine 2013; 5(1): 6–13.
- Close D.M., Xu T., Sayler G.S., Ripp S. In vivo bioluminescent imaging (bli): noninvasive visualization and interrogation of biological processes in living animals. Sensors (Basel) 2011; 11(1): 180–206.
- Riedel S.S., Mottok A., Brede C., Bäuerlein C.A., Jordán Garrote A.L., Ritz M., et al. Non-invasive imaging provides spatiotemporal information on disease progression and response to therapy in a murine model of multiple myeloma. PLoS One 2012; 7(12): 52398.
- Burkhardt J.K., Hofstetter C.P., Santillan A., Shin B.J., Foley C.P., Ballon D.J., et al. Orthotopic glioblastoma stem-like cell xenograft model in mice to evaluate intra-arterial delivery of bevacizumab: from bedside to bench. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19(11): 1568–1572.
- Poeschinger T., Renner A., Weber T., Scheuer W. Bioluminescence imaging correlates with tumor serum marker, organ weights, histology, and human DNA levels during treatment of orthotopic tumor xenografts with antibodies. Mol Imaging Biol 201; 15(1): 28–39.
- Ramani P., Hart I.R., Balkwill F.R. The effect of interferon on experimental metastases in immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice. Int J Cancer 1986; 37(4): 563–568.










