Antihypoxic and Neuroprotective Properties of BDNF and GDNF in vitro and in vivo Under Hypoxic Conditions
The aim of the investigation was to assess antihypoxic and neuroprotective properties of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) during in vitro and in vivo hypoxia models.
Materials and Methods. In vitro studies were performed using hippocampal cells dissociated from 18-days embryonic CBA mice and cultured on multielectrode arrays (MEA60). Hypoxia modeling was performed on day 14 of culture development in vitro by replacing the normoxic culture medium with a medium containing low oxygen for 10 min. In vivo experiments were carried out on C57BL/6j male mice weighing 18–20 g. For acute hypobaric hypoxia a vacuum flow-through chamber was used at the ambient temperature of 20–22°C. We studied the resistance of animals to hypoxia, as well as their spatial memory retention in the Morris water maze upon expiration of 24 h following hypoxia model.
Results. The carried out in vitro and in vivo experiments revealed that BDNF and GDNF have strong antihypoxic and neuroprotective effects. Preventive application of BDNF plus GDNF before testing in the Morris water maze, contributed less animal resistance and retention of spatial memory as well as the viability of cells in dissociated hippocampal cultures was decreased in comparison with the isolated effect each of these factors.
Conclusion. Application of BDNF in combination with GDNF under hypoxic conditions reduces the positive individual effect these neurotrophic factors.
To protect brain cells from hypoxia-induced injuries, various therapeutic approaches based on the endogenic substances or their derivatives for the neurologic status correction, are being currently developed. According to modern views, neurotrophic factors play a critical role in the functioning of brain neural networks in the stages of development and in a postnatal period [1, 2]. Neurotrophins contribute to viability of brain cells with the high metabolic rate under the influence of stress-factors. Protective mechanisms of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) are interconnected and realized through the unidirectional homeostasis reactions of neural networks. BDNF and GDNF interaction with the highly selective receptors on a cellular surface leads to the activation of protective MAP kinases (MAPK) and subsequent launching signaling pathways [3–7]. However, the question concerning the presupposed synergism of these neurotrophins remains open. Our previous in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrated that preventive application of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces negative effects of hypoxia [8, 9]. BDNF and GDNF combined application can strengthen the activation of intracellular cascades and, therefore, increase protective effects of each factor.
The aim of the investigation was to assess antihypoxic and neuroprotective properties of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in hypoxia models in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and Methods
In vitro experiments. In vitro studies were performed using hippocampal cells dissociated from 18-day embryonic CBA mice. The primary rules of keeping and caring for test animals were in accordance with the Russian Federation Ministry of Public Health Decree No.267 as of June 19, 2003 “On Good Laboratory Practices of the Russian Federation” and agreed with the Ethics Committee of Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy.
The cells were dissociated by 0.25% Trypsin (Gibco, USA) application to the hippocampal tissue and then resuspended in neurobasal medium Neurobasal™ (Invitrogen, USA) with B27 (Invitrogen), glutamine (Invitrogen), fetal bovine serum (PanEco, Russia). Dissociated hippocampal cells were seeded onto MEAs (Multichannel Systems, Germany) containing 60 microelectrodes and were cultured according to the previously developed protocol [10] during 30 days in vitro. MEAs were sterilized by UF-radiation and pre-treated with the adhesion-promoting molecule polyethyleneimine (Sigma, USA). The initial density of cells placed on each array was 9000 cells/mm2. The cells were cultured under constant conditions of 35.5°C and 5% CO2 at saturating humidity in a cell culture incubator [10]. All the signal analyses were performed using custom-made software MC Rack™ (Multichannel Systems, Germany) and the Matlab®.
Hypoxia modeling was performed on day 14 of culture development in vitro by replacing the normoxic cultural medium with a medium containing low oxygen for 10 min. The oxygen was displaced from the medium in sealed chamber in which the air was replaced with an inert gas. The experimental substances were added to the medium 20 min before hypoxia. In the control group hypoxia was induced without additional treatment. The parameters characterizing the response of the primary hippocampal culture to hypoxia were recorded 2 h after hypoxia and the following 7 days.
Cell viability detection. The viability of dissociated hippocampal cells was evaluated according to the percentage ratio between the number of dead cells stained by propidium iodide (Sigma, Germany) and the total number of cells stained by bisBenzimide (Invitrogen, USA) for 7 days after hypoxia.
In vivo experiments. The studies were performed on 86 C57BL/6j mature male mice weighing 18–20 g. The primary rules of keeping and caring for experimental animals were in accordance with the Russian Federation Ministry of Public Health Decree No.708H as of August 23, 2010 "On Good Laboratory Practices in the Russian Federation", and in accordance with the Ethical Principles of the European Convention for protection of vertebrate animals, used with experimental and other scientific purposes (the Convention took place in Strasbourg on March 18, 1986 and was confirmed in Strasbourg on June 15, 2006). The said rules and protocols as well agreed with the Ethics Committee of Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy.
Research techniques. Foracute hypobaric hypoxia model a vacuum flow-through chamber was used at the ambient temperature of 20–22oC. Mice were placed under conditions corresponding altitude 10 000–10 500 m (170–185 mm Hg) with a lifting speed 183 m/s [11]. The animal resistance to hypoxia was evaluated by the lifetime on the “height” (Tlife, min), which was calculated from the moment of lifting to the “height” and until animal death or the second agonal breath; loss of posture time (Tlop, min) — a period starting at the moment of lifting in the chamber and until the moment, when an animal takes a lateral position and loses its ability to maintain physiological posture. Tlife was used fordetermination the animal resistance to hypoxia, dividing the mice into three corresponding groups: low-resistant subjects (Tlife — less than 3 min), mid-resistant (Tlife — between 3 and 9 min) and high-resistant ones (Tlife — over 9 min without visible signs of hypoxic brain damage).
Cr — resistance coefficient was used to compare efficiency of the antihypoxic actions, calculated based on the animal viability under condition on the “height” during 10 min of acute hypoxia.
Cr=(a/b+1)/(c/d+1):
where a and b are a number of survivors in the experimental and control groups; c and d are a total number of animals in the experimental and control groups [11].
To assess neuroprotective properties of the neurotrophic factors the animals passed the navigation training in Morris water maze. This test was carried out by the standard technique [12], modified for mice (diameter of the pool — 90 cm, diameter of the platform under water — 10 cm). The motion trajectory was recorded by special video equipment; data analysis was performed using MouseTrack and Traceman algorithms developed in Matlab®. The animals were selected by their ability to spatial memory formation and learning. Learning efficiency factors included the time, needed for a problem solving, and a free swimming trajectory.
Quantitative assessment of this criterion was performed according to the Cr, which equals to the ratio between the time periods, spent to find the platform (viz. latent periods) during the first session, and the latent time periods during any other subsequent sessions (Cr2 — reflects task completion during the second learning session in comparison with the first session; Cr3 — reflects task completion during the third learning session in comparison with the first session, etc.). The highest Cr reflects the quickest process of learning.
The long-term memory retention test was conducted during 24 h after hypoxia. The test consisted of 1 assay with 60 s duration without the platform in the maze. The delayed coefficient of retention (dCr) was calculated as the time period spent by an animal in the quadrant where the platform was previously situated to the total pastime in the maze. In case, an animal spent 23–27% of the total maze time in the platform quadrant, it was considered to be normal [13, 14]. The free-swimming trajectory when searching for the platform was evaluated as well.
Statistical analysis. Significance of differences between the experimental groups was assessed by means of ANOVA software. Differences between groups were considered significant if the corresponding pvalue was less than 0.05.
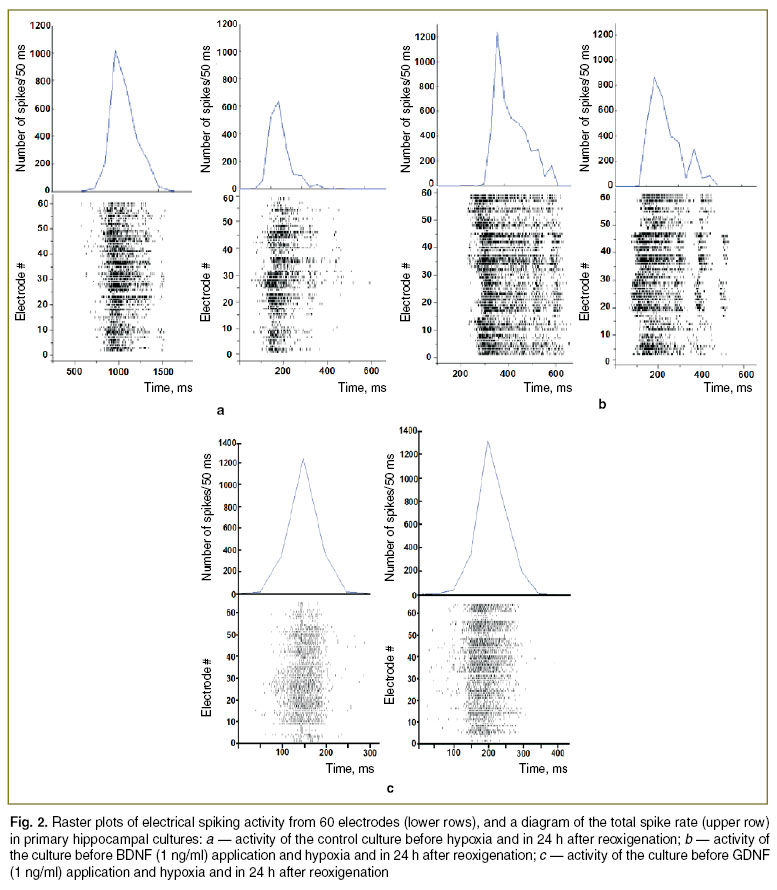
Results. First, we investigated the influence of neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF) on the preservation of spontaneous bioelectrical activity in dissociated hippocampal cultures. The spontaneous bioelectrical activity of primary hippocampal cultures had stabilized by day 14 in vitro [10]. Analysis of morphofunctional structure of neural networks revealed stabilization of the main parameters of bioelectrical activity (number of small bursts, number of spikes per burst) by day 14 in vitro, as well as presence of the complex axon-dendritic and axon-somatic synapses in dissociated hippocampal cultures [15, 16]. Hypoxia leads to irreversible destructive changes in the functional network activity of the primary hippocampal cultures [8, 17]. There was an almost complete loss of spontaneous network activity by day 7 of the post-hypoxic period. Only 32.4% of the control cultures save network activity with an altered pattern of small network bursts (Fig. 1).
Preventive application of neurotrophic factors BDNF (1 ng/ml) and GDNF (1 ng/ml) partially neutralizes the negative hypoxic effects on the spontaneous bioelectrical activity. Experiments revealed that neurotrophic factors is significantly (р<0.05) increases the number of small bursts in 24 h after hypoxia. The analysis of activity patterns performed the day after hypoxia revealed that preventive application of the neurotrophic factors (BDNF, 1 ng/ml and GDNF, 1 ng/ml) contribute to network structure maintenance, and, therefore, to preserve the morphofunctional structure of neural networks in dissociated hippocampal cultures (Fig. 2).
Studies, conducted in the post-hypoxic period, showed that in GDNF (1 ng/ml) group of cultures the average number of spikes per burst was significantly (р<0.05) higher, than in the “Hypoxia” group 3 days after hypoxia: 2213.54±256.43 and 465.67±97.21, respectively. Moreover, the number of small bursts in all experimental groups was significantly (р<0.05) less in comparison with the period before hypoxia.
By the day 7 of the post-hypoxic period in all groups, which received preventive doses of both neurotrophic factors, there was a restoration in the number of small bursts and in the average number of spikes per burst up to the baseline (no statistically significant differences with the activity of cultures before hypoxia). At the same time parameters of spontaneous bioelectrical activity in groups with preventive application of neurotrophic factors were significantly (p<0.05) higher than in the “Hypoxia” group.
The next stage was to assess viability of dissociated hippocampal cells after acute normobaric hypoxia modeling. It was shown that 1 ng/ml concentration of each neurotrophic factors have significant cytoprotective effect which leads to decreased the number of dead cells during 7 days of the post-hypoxic period.
Analysis of the combined neurotrophins action (BDNF, 1 ng/ml + GDNF, 1 ng/ml) did not reveal any increase in cytoproteсtive effect (Fig. 3). We note that in an experimental group with both neurotrophins application there was a higher percentage of dead cells in comparison with the groups with isolated factors application. Thus, the research of viability of cells in the primary hippocampal culture did not reveal any increase antihypoxic effect by combining neurotrophic factors.
Study of dose-dependent effects of the neurotrophic factors did not observe any changes in number of dead cells for 7 days after hypoxia. Furthermore, increase of BDNF concentration to 10 ng/ml in the post-hypoxic period leads to the tendency decrease the number of dead cells (1 ng/ml — 12.34±3.54%, 10 ng/ml — 9.65±2.87%).
On the other hand, the increase of GDNF concentration did not cause significant increase in the number of dead (propidium iodide — positive) cells on day 7 after hypoxia (1 ng/ml — 11.15±3.14%, 10 ng/ml — 14.09±4.28%).
The following step was to assess the influence of the neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF) on animal resistance to acute hypobaric hypoxia. It was shown that preventive injection of the neurotrophic factors increases animal resistance to acute hypobaric hypoxia (Table 1). BDNF (4 μg/kg) and GDNF (4 μg/kg) intranasal application significantly increases the lifetime on the “height”.
 Table 1. The main parameters of animal resistance to acute hypobaric hypoxia Table 1. The main parameters of animal resistance to acute hypobaric hypoxia
|
Particular attention is given to resistance parameters in GDNF animal group (4 μg/kg). In spite of significant (р<0.05) increase in the lifetime on the “height” and a higher resistance coefficient in this group, the loss of posture time, characterizing the state of animal reflex reaction, appeared to be the lowest. We note that high concentration of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor decrease the animal resistance. The group with a preventive dose of GDNF (40 μg/kg) did not reveal any significant differences in resistance comparing with the control group.
Injection of BDNF with GDNF significantly reduces animal resistance to acute normobaric hypoxia conditions. This group demonstrated the lowest coefficient of resistance. Thus, the study revealed the antagonistic effect of both neurotrophic factors simultaneously application.
The analysis of the processes of spatial memory retention in Morris water maze after episode of acute hypobaric hypoxia was conducted in order to assess neuroprotective effects of BDNF and GDNF. The main mice strategies of searching the hidden platform in the water maze were determined as following: 1) directachieving the goal — an experimental animal goes straight to the platform (time in water 3–10 s); 2) active search — an experimental animal swims around (circularorradialtrajectory), trying to find the platform (time in water 10 to 20 s); 3) chaotic search — no obvious strategy necessary to achieve the goal (time in water more than 20 s); 4) negative result — an experimental animal is not able to find the platform.
At the first testing in the maze, the most of animals chose chaotically type of searching the platform. The animals swam close to the walls of the pool, which could be explained by genetic behavioral tactics called thigmotaxis. We note that during the subsequent attempts the processes of spatial memory formation in experimental mice were developed. In the process of learning animals required less time in order to find the platform and chose direct searching the goal, characterized, as a rule, by circularorradialtrajectory.
Delayed testing in the water maze showed a slight long-term memory disturbance in mice a day after acute hypobaric hypoxia. The decrease of dCr values in comparison with intact group was not significant (Table 2). Injection of Reamberin as an antihypoxic drug did not contribute to the processes of spatial memory after acute hypobaric hypoxia (dCr was 25.6±3.1). However, application of BDNF and GDNF prevents spatial memory lesion in the post-hypoxic period. The best results in dCr parameter were observed in experimental groups received intranasal doses of BDNF (40 μg/kg) and GDNF (40 μg/kg) (dCr “BDNF, 40 μg/kg” — 35.5±4.1, dCr “GDNF, 40 μg/kg” — 36.06±4.3). It should be noticed that dCr in both groups was significantly higher in comparison with the control group values and even the values of “Reamberin” group. Intranasal injection of small doses of the neurotrophic factors (4 mg/kg) contributed as well to the decrease of negative hypoxic effects and retention of spatial memory. However, detected tendencies did not reveal any significant differences (dCr “BDNF, 4 μg/kg” — 30.6±3.9, dCr “GDNF, 4 μg/kg” — 33.54±3.98).
 Table 2. Delayed coefficient of the long-term memory retention level for mice after acute hypobaric hypoxia (M±m) Table 2. Delayed coefficient of the long-term memory retention level for mice after acute hypobaric hypoxia (M±m)
|
Discussion. Hypoxia is considered to be one of the main factors involved in ischemic brain damage. The pathological reactions triggered by oxygen starvation are associated with an uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, disturbances in cellular energy levels, and the activation of free radical processes that stimulate apoptosis. The negative effects of oxygen deficiency are particularly important in the nervous system, where the loss of individual network elements can cause irreversible damage of functional neural networks. Therefore, the study of protective mechanisms of brain cells against oxygen deprivation is one of the most important issues in modern neurobiology and biomedicine.
In vitro and in vivo data demonstrate that BDNF and GDNF have strong antihypoxic and neuroprotective effects. Preventive application of BDNF or GDNF partially neutralizes negative hypoxic effects at the cellular and organismic levels.
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor can actively change neuronal metabolism in an adult organism. BDNF is connected with two types of membrane receptors: the low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR), or p75, and the high-affinity tyrosine-kinase receptor B — TrkB [18]. It is assumed, that protective mechanisms of this neurotrophin are associated with the ability of a mature BDNF molecule to connect with TrkB receptors and activate intracellular signaling cascades [7, 19]. One of the signaling pathways associated with survival during hypoxia is the activation of the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-кB) protein complex. NF-кB1 responds to the expression of proteins from the Bcl2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) and IAP (Inhibitors of Apoptosis) [20]. Moreover, NF-kB1 is the main inhibitory agent of apoptosis along with a number of other factors (for example, c-jun and cIAP1) [21]. Increased NF-кB1 mRNA synthesis induced by BDNF is one possible mechanism through which cells can alter their metabolism in response to low oxygen levels. Moreover, antihypoxic effects of this neurotrophin can be connected with a direct BDNF action upon the mitochondrial system of cells. Investigation of BDNF effect on oxygen metabolism in brain mitochondria showed that BDNF concentration-dependent increases the respiratory index (efficiency parameter of the respiratory chain, ATP synthesis and organella integrity) [22, 23]. Increase of the respiratory index promotes adaptation of cells to oxygen starvation.
The glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor along with some other neurotrophins participates in the regulation processes of neural networks in an adult organism. The mechanisms of GDNF are associated with activation of complex neuron–glial interactions. GDNF action is mediated by activation of the universal GFR1 multicomponent receptors [24]. Such receptor does not have any intracellular domain, therefore, it acts as a signal transmitter to other proteins, in particular, to tyrosine-kinase protein RET. At the next stage RET activates some intracellular signaling cascades: RAS/MAPK, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PK3-K)/Akt, phospholipase C [4, 5]. Launch of RAS/MAPK, PK3-K/Akt signaling mechanisms leads to increase survival of various neuronal populations [5]. GDNF has a local effect (at the place of synthesis), as well as the remote one [25, 26]. Maintaining of the functional activity of neuronal networks and resistance of animals to oxygen starvation can be related to activation of complex and universal GDNF-associated signaling systems. Thus, this neurotrophin is the unique signaling molecule, which does not only contribute to maintenance of individual neuronal viability, but also integrates metabolic reactions of individual components of the neuron-glial network into one functional structure.
The studies show that the application of BDNF and GDNF may significantly reduce the negative consequences of hypoxic brain damage.
Conclusion. The brain-derived and the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factors have strong antihypoxic and neuroprotective effects. In vitro and in vivo experiments showed that preventive applicationof BDNF in combination with GDNF under hypoxic conditions reduces the positive individual effect of these neurotrophic factors.
Acknowledgments. This research was supported by grants from the Russian Foundation of Basic Research (No.13-04-01871, No.13-04-12067, No.14-04-31601), partially supported by a grant (August 27, 2013, No.02.B.49.21.0003) from the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation and Lobachevsky State University of Nizhni Novgorod, Federal target program “A unique scientific apparatus to study information processes in brain using optogenetic techniques” (December 1, 2014, No.14.591.21.0004).
Conflict of Interests. The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
References
- Lin S., Ye S., Huang J., Tian Y., Xu Y., Wu M., Wang J., Wu S., Cai J. How do Chinese medicines that tonify the kidney inhibit dopaminergic neuron apoptosis? Neural Regen Res 2013; 8(30): 2820–2826, http://dx.doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.30.004.
- Wei L., Zhang J., Xiao X.B., Mai H.X., Zheng K., Sun W.L., Wang L., Liang F., Yang Z.L., Liu Y., Wang Y.Q., Li Z.F., Wang J.N., Zhang W.J., You H. Multiple injections of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells through the tail vein improve microcirculation and the microenvironment in a rat model of radiation myelopathy. J Transl Med 2014; 12(1): 246, http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12967-014-0246-6.
- Han B.H., Holtzman D.M. BDNF protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury in vivo via the ERK pathway. J Neurosci 2000; 20(15): 5775–5781.
- Airaksinen M.S., Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3(5): 383–394, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn812.
- Sariola H., Saarma M. Novel functions and signalling pathways for GDNF. J Cell Sci 2003; 116(Pt 19): 3855–3862, http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00786.
- Hetman M., Gozdz A. Role of extracellular signal regulated kinases 1 and 2 in neuronal survival. Eur J Biochem 2004; 271(11): 2050–2055, http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04133.x.
- Sakharnova T.A., Vedunova M.V., Mukhina I.V. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its role in the functioning of the central nervous system. Neurochemical Journal 2012; 6(4): 251–259, http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1819712412030129.
- Vedunova М.V., Sakharnova Т.А., Mitroshina E.V., Mukhina I.V. Antihypoxic properties of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the modeling of hypoxia in dissociated hippocampal cultures. Sovremennye tehnologii v medicine 2012; 4: 17–23.
- Sakharnova T.A., Vedunova M.V., Mitroshina E.V., Mukhina I.V. The antihypoxic and neuroprotective action of neurotrophic factors BDNF and GDNF during acute hypobaric hypoxia in vivo. Biomeditsinskaya radioelektronika 2014; 4: 71–72.
- Mukhina I.V., Kazantsev V.B., Khaspeckov L.G., Zakharov Yu.N., Vedunova M.V., Mitroshina E.V., Korotchenko S.A., Koryagina E.A. Multielectrode matrices — new possibilities in investigation of the neuronal network plasticity. Sovremennye tehnologii v medicine 2009; 1: 8–15.
- Metodicheskie rekomendatsii po eksperimental'nomu izucheniyu preparatov, predlagaemykh dlya klinicheskogo izucheniya v kachestve antigipoksicheskikh sredstv [Guidelines on experimental study of drugs offered for clinical study as antihypoxic agents]. Pod red. Luk’yanovoy L.D. [Luk’yanova L.D. (editor)]. Moscow; 1990.
- Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 1984; 11(1): 47–60, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4.
- Mitroshina E.V., Vedunova M.V., Mironov A.A., Saharnova T.A., Pimashkin A.S., Bobrov M.Yu., Khaspekov L.G., Mukhina I.V. Neuroprotective effect of endacannabinoid N-arachidonoyldopamine in acute hypobaric hypoxia. Nevrologicheskiy vestnik im. Bekhtereva 2012; 1: 14–19.
- D’Hooge R., De Deyn P.P. Application for the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 2001; 36(1): 60–90.
- Agrba E.A., Mukhina I.V. Spatio-temporal characteristics of neuronal network activity of primary hippocampal cultures. Vestnik Nizhegorodskogo universiteta im. N.I. Lobachevskogo 2013; 4(1): 139–144.
- Shirokova О.М., Frumkina L.Е., Vedunova М.V., Mitroshina Е.V., Zakharov Y.N., Khaspekov L.G., Mukhina I.V. Morphofunctional patterns of neuronal network developing in dissociated hippocampal cell cultures. Sovremennye tehnologii v medicine 2013; 5(2): 6–13.
- Vedunova M.V., Mitroshina E.V., Sakharnova T.A., Bobrov M.Yu., Bezuglov V.V., Khaspekov L.G., Mukhina I.V. Effect of N-arachidonoyl dopamine on activity of neuronal network in primary hippocampus culture upon hypoxia modelling. Bull Exp Biol Med 2014; 156(4): 461–464, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2374-7.
- Patapoutian A., Reichardt L.F. Trk receptors: mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001; 11(3): 272–280.
- Chen A., Xiong L.J., Tong Y., Mao M. The neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Biomed Rep 2013; 1(2): 167–176, http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/br.2012.48.
- LaСasse E.C., Baird S., Korneluk R.G., MacKenzie A.E. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 1998; 17(25): 3247–3259.
- Bogdał M.N., Hat B., Kochanczyk M., Lipniacki T. Levels of pro-apoptotic regulator Bad and anti-apoptotic regulator Bcl-xL determine the type of the apoptotic logic gate. BMC Syst Biol 2013; 7: 67, http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-7-67.
- Markham A., Cameron I., Bains R., Franklin P., Kiss J.P., Schwendimann L., Gressens P., Spedding M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated effects on mitochondrial respiratory coupling and neuroprotection share the same molecular signaling pathways. Eur J Neurosci 2012, 35(3): 366–374, http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07965.x.
- Markham A., Cameron I., Franklin P., Spedding M. BDNF increases rat brain mitochondrial respiratory coupling at complex I, but not complex II. Eur J Neurosci 2004, 20(5): 1189–1196,http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03578.x.
- Jing S., Wen D., Yu Y., Holst P.L., Luo Y., Fang M., Tamir R., Antonio L., Hu Z., Cupples R., Louis J.C., Hu S., Altrock B.W., Fox G.M. GDNF-induced activation of the ret protein tyrosine kinase is mediated by GDNFR-alpha, a novel receptor for GDNF. Cell 1996, 85(7): 1113–1124, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81311-2.
- Rind H.B., Butowt R., von Bartheld C.S. Synaptic targeting of retrogradely transported trophic factors in motoneurons: comparison of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and cardiotrophin-1 with tetanus toxin. J Neurosci 2005, 25(3): 539–549, http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4322-04.2005.
- Tsui C.C., Pierchala B.A. The differential axonal degradation of Ret accounts for cell-type-specific function of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor as a retrograde survival factor. J Neurosci 2010; 30(15): 5149–5158, http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5246-09.2010.